The name of the competition under which the program is being implemented: The project is being implemented as part of the grant financing of young scientists under the «Zhas Galim» project, with the support of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Project Supervisor: Lyazat Liakyn.
Identifiers:
- Scopus Author ID:58071261100,
- ORCID ID: https://orcid.org/0009-0006-8255-7356.
Project research team
| № | Full name | Full name | Identifiers (Scopus Author ID, Researcher ID, ORCID, if available) and links to relevant profiles |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Zh.S. Onalbayeva | Consultant |
Author ID Scopus – 56512368600, |
Project Abstract:
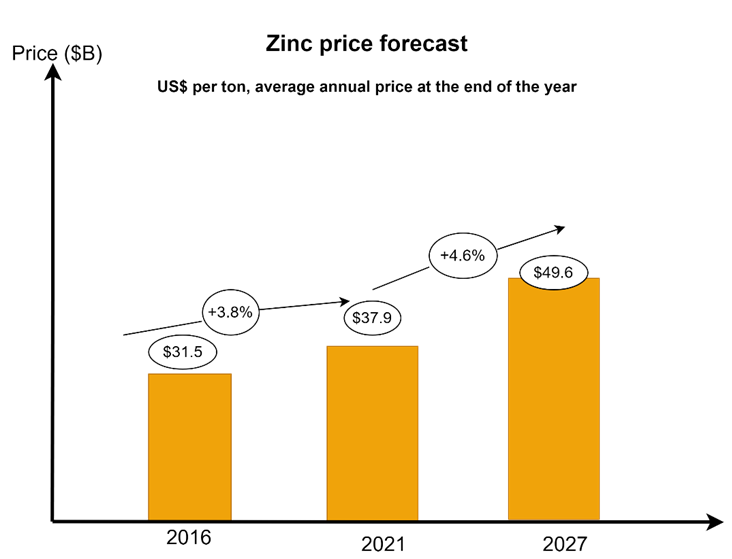
According to the latest research by scientists, in the coming decades, the shortage of raw materials for many basic metals will lead to a sharp rise in their value, for example, the currently relatively cheap zinc and iron may soon become valuable metals. Zinc reserves will be exhausted by 2030, and according to the forecasts presented, we can expect a rapid rise in metal prices in the near future.
About 85% of the world's zinc is currently produced using RLE (roasting-leaching-electrolysis) processes, which in turn leaves 0.5-0.9 tons of dry jarosite as waste for every ton of zinc produced. If zinc production in 2024 will increase to 14 million tons, then up to 7-12.6 million tons of environmentally hazardous, unusable jarosite will enter the environment in the form of waste.
From the above data we can draw the following conclusion: since the cost of zinc is increasing due to the reduction of raw materials, the development of effective technologies for obtaining high quality products from low-quality raw materials of complex composition is an urgent task.
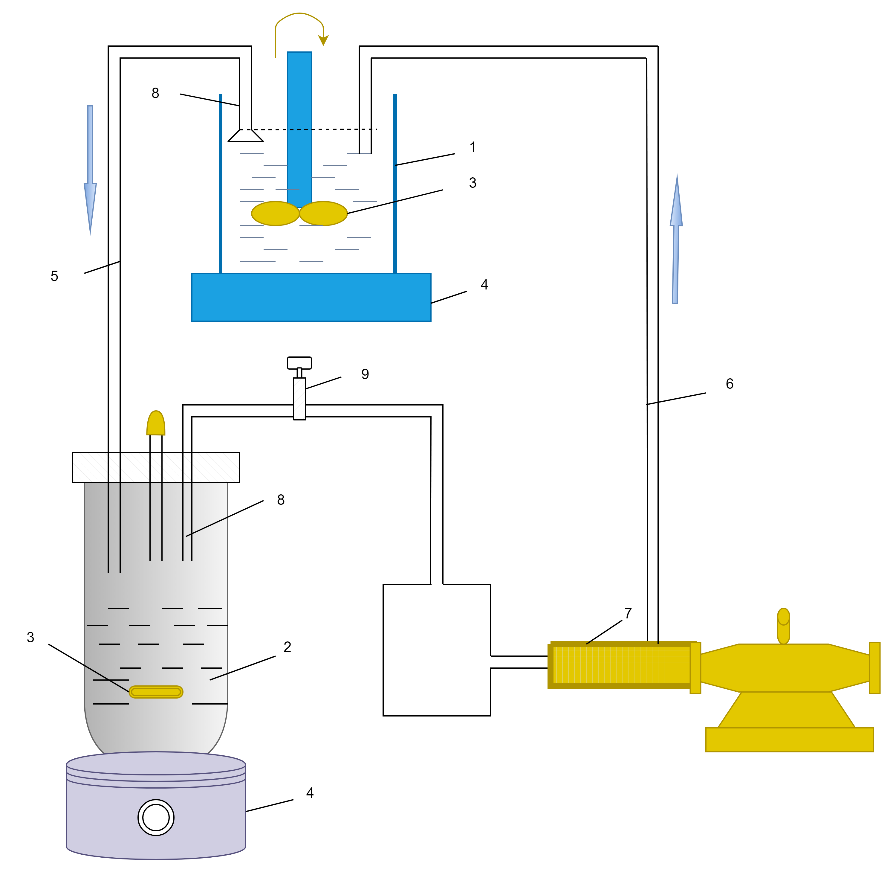
One of the main reasons of attraction of low-quality mineral raw materials into the process of metallurgical processing is depletion of high-quality ores of non-ferrous and rare metals. As a result of direct leaching of such raw materials by atmospheric hydrometallurgical methods, solutions characterized by 15-16 times excessive amount of impurities, especially iron in solution, are formed. Purification of such solutions from impurities is currently very problematic. The relevance of this issue is confirmed by the analysis of scientific and technical literature sources and experience of enterprises on research and application of hydrometallurgical technologies of zinc-containing solutions purification from impurities. Among all various methods it is of interest to use the technology of electro-oxidation of iron ions in zinc-containing sulfate solutions, it has the following advantages:
- no additional elements and compounds are added to the cleaning solution, which means there is no need to purchase or prepare, deliver and store them;
- if the process of electro-oxidation of Fe2+ ion to Fe3+ ion is carried out at the anode using an anion-exchange membrane electrolyzer, the cathodic cleaning process of copper and cadmium solutions can be carried out at the cathode at the same time.
- Iron ions in the solution are released in the form of hematite, hematite is an environmentally friendly substance. The economic efficiency can also be ensured by its suitability for use as a building material.
Project Goal: Purification of complex zinc sulfate solution from impurities and separation of iron from the solution in the form of hematite.
Expected and achieved project results:
| Year | The obtained research results. Publications (with links to them) and patents; information for potential users. |
|---|---|
| 2024 |
Patent information is searched. New articles and patents presented in open literature on the topic of research are found, and a literature review is written on the topic of research on the physico-chemical research on the purification of complex zinc sulfate solution and on the treatment of iron-containing waste from zinc production. |
| 2025 |
Investigation of the chemical composition and structure of zinc sulfate solution with a complex composition in zinc production, iron dross obtained after purification of zinc sulfate solution from iron, using chemical, spectral, X-ray phase analysis and raster electron analysis with a microanalyzer. Development of a technological plan for cleaning zinc sulfate solution with a complex composition. Development of an optimal technological scheme for the processing of iron slag in the form of hematite obtained after iron removal from a complex zinc sulfate solution. Studying the kinetics of separation of iron ions in the form of hematite from zinc sulfate solution, construction of membrane electrolyzer unit for direct electrochemical oxidation of Fe2+ ions in zinc sulfate solution; study of the kinetics of the process of oxidizing iron ions in an anion-exchange membrane electrolyzer; after electrooxidation of complex composition zinc sulfate solution, send the resulting solution to precipitation in the presence of calcium oxide, and determine the chemical composition and structural formula of the resulting cake. Creating a blueprint for the separation of iron-containing industrial waste in the form of magnetite in zinc production. Construction of a device for separation of iron-containing production waste in the form of magnetite in zinc production. Investigation of the process of separation of iron-containing waste in the form of magnetite in zinc production by physico-chemical methods. |
| 2026 |
As a result of laboratory tests, the product will be lower than the market value, and this technology will be introduced to offer to potential investors. Experimental data on waste-free integrated technology of zinc and energy industry waste processing are obtained. An act of extended laboratory research is obtained at the enterprise operating "Kazzinc" JSC. |
Infographics
Date of last changes:16.01.2025